ES 2015(ES6) 复习总结 part2
String.includes()
includes()方法用于判断一个字符串是否包含在另一个字符串内,根据情况返回true或false
includes()是区分大小写的。
'Blue Whale'.includes('blue'); // returns false
兼容补丁:
if (!String.prototype.includes) {
String.prototype.includes = function(search, start) {
'use strict';
if (typeof start !== 'number') {
start = 0;
}
if (start + search.length > this.length) {
return false;
} else {
return this.indexOf(search, start) !== -1;
}
};
}
//举例
var str = 'To be, or not to be, that is the question.';
console.log(str.includes('To be')); // true
console.log(str.includes('question')); // true
console.log(str.includes('nonexistent')); // false
console.log(str.includes('To be', 1)); // false
console.log(str.includes('TO BE')); // false
String.startWith() & String.endsWith()
startWith()
startsWith()用来判断当前字符串是否以另外一个给定的子字符串开头,并根据判断结果返回true 或false
第一个参数为要搜索的字符串,第二个参数为第一个参数开始的位置,默认为0
兼容补丁:
if (!String.prototype.startsWith) {
Object.defineProperty(String.prototype, 'startsWith', {
value: function(search, pos) {
pos = !pos || pos < 0 ? 0 : +pos;
return this.substring(pos, pos + search.length) === search;
}
});
}
举例
var str = "To be, or not to be, that is the question.";
alert(str.startsWith("To be")); // true
alert(str.startsWith("not to be")); // false
alert(str.startsWith("not to be", 10)); // true
endsWith
endsWith()用来判断当前字符串是否是以另外一个给定的子字符串”结尾“,根据判断结果返回true或false
第一个参数为要搜索的子字符串,第二个参数作为要检验的字符串的长度(从头开始计算)
兼容:
if (!String.prototype.endsWith) {
String.prototype.endsWith = function(search, this_len) {
if (this_len === undefined || this_len > this.length) {
this_len = this.length;
}
return this.substring(this_len - search.length, this_len) === search;
};
}
举例
var str = "To be, or not to be, that is the question.";
alert( str.endsWith("question.") ); // true
alert( str.endsWith("to be") ); // false
alert( str.endsWith("to be", 19) ); // true
与Array有关的新方法
Array.from()
Array.from() 方法从一个类似数组或可迭代对象创建一个新的,浅拷贝的数组实例。
console.log(Array.from('foo'));
// expected output: Array ["f", "o", "o"]
console.log(Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x + x));
// expected output: Array [2, 4, 6]
使用语法: Array.from(arrayLike[, mapFn[, thisArg]])
第一个参数为 arrayLike。为想要转换成数组的伪数组对象或可迭代对象
第二个参数mapFn可选, 如果指定了该参数,新数组中的每个元素会执行该回调函数
第三个参数thisArg可选。 执行回调函数mapFn时的this对象
返回值为一个新的数组实例
//从String生成数组
Array.from('foo');// [ "f", "o", "o" ]
//从Set生成数组
const set = new Set(['foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'foo']);
Array.from(set);// [ "foo", "bar", "baz" ]
//从Map生成数组
const map = new Map([[1, 2], [2, 4], [4, 8]]);
Array.from(map);// [[1, 2], [2, 4], [4, 8]]
const mapper = new Map([['1', 'a'], ['2', 'b']]);
Array.from(mapper.values());// ['a', 'b'];
Array.from(mapper.keys());// ['1', '2'];
//在Array.from()中使用箭头函数
数组去重合并
function combine(){
let arr = [].concat.apply([], arguments); //没有去重复的新数组
return Array.from(new Set(arr));
}
var m = [1, 2, 2], n = [2,3,3];
console.log(combine(m,n)); // [1, 2, 3]
Array.keys()
keys() 方法返回一个包含数组中每个索引键的Array Iterator对象。
举例
var arr = ["a", , "c"];
var sparseKeys = Object.keys(arr);
var denseKeys = [...arr.keys()];
console.log(sparseKeys); // ['0', '2']
console.log(denseKeys); // [0, 1, 2]
Array.find()
find() 方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的值。否则返回 undefined。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const found = array1.find(element => element > 10);
console.log(found);
// expected output: 12
使用方法: arr.find(callback[, thisArg])
callback: 在数组每一项上执行的函数,接受三个参数( element: 当前遍历到的元素;index(可选):当前遍历到的索引;array(可选): 数组本身)
thisArg(可选):执行回调时用作this的对象
find对数组中每一项元素执行一次callback,所以复杂度还是很高的。
find方法不会改变数组
举例
var inventory = [
{name: 'apples', quantity: 2},
{name: 'bananas', quantity: 0},
{name: 'cherries', quantity: 5}
];
function findCherries(fruit) {
return fruit.name === 'cherries';
}
console.log(inventory.find(findCherries)); // { name: 'cherries', quantity: 5 }
// 寻找数组中的质数
function isPrime(element, index, array) {
var start = 2;
while (start <= Math.sqrt(element)) {
if (element % start++ < 1) {
return false;
}
}
return element > 1;
}
console.log([4, 6, 8, 12].find(isPrime)); // undefined, not found
console.log([4, 5, 8, 12].find(isPrime)); // 5
Array.findIndex()
findIndex()方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的索引。若没有找到对应元素则返回-1。
使用方法: arr.findIndex(callback[, thisArg])
callback: 在数组每一项上执行的函数,接受三个参数( element: 当前遍历到的元素;index(可选):当前遍历到的索引;array(可选): 数组本身)
thisArg(可选):执行回调时用作this的对象
例子
//查找数组中首个质数元素的索引
function isPrime(element, index, array) {
var start = 2;
while (start <= Math.sqrt(element)) {
if (element % start++ < 1) {
return false;
}
}
return element > 1;
}
console.log([4, 6, 8, 12].findIndex(isPrime)); // -1, not found
console.log([4, 6, 7, 12].findIndex(isPrime)); // 2
New Math Methods
Math.trunc()
将数字的小数部分去除,只保留整数部分。不管参数是正数还是负数,仅仅是删除掉数字的小数部分和小数点
传入该方法的参数会被隐式转换成数字类型
Math.trunc(13.37) // 13
Math.trunc(42.84) // 42
Math.trunc(0.123) // 0
Math.trunc(-0.123) // -0
Math.trunc("-1.123") // -1
Math.trunc(NaN) // NaN
Math.trunc("foo") // NaN
Math.trunc() // NaN
Math.sign()
返回一个数字的符号 ,指示数字是正数 负数 还是 零
此函数共有5种返回值, 分别是 1, -1, 0, -0, NaN. 代表的各是正数, 负数, 正零, 负零, NaN。
传入该函数的参数会被隐式转换成数字类型。
Math.sign(3); // 1
Math.sign(-3); // -1
Math.sign("-3"); // -1
Math.sign(0); // 0
Math.sign(-0); // -0
Math.sign(NaN); // NaN
Math.sign("foo"); // NaN
Math.sign(); // NaN
Math.cbrt()
**Math.cbrt()** 函数返回任意数字的立方根.
cbrt 是 “cube root” 的缩写, 意思是立方根.
Math.cbrt(NaN); // NaN
Math.cbrt(-1); // -1
Math.cbrt(-0); // -0
Math.cbrt(-Infinity); // -Infinity
Math.cbrt(0); // 0
Math.cbrt(1); // 1
Math.cbrt(Infinity); // Infinity
Math.cbrt(null); // 0
Math.cbrt(2); // 1.2599210498948734
Math.log2()
**Math.log2()** 函数返回一个数字以 2 为底的对数.
如果传入的参数小于 0, 则返回 NaN.
Math.log2(2) // 1
Math.log2(1024) // 10
Math.log2(1) // 0
Math.log2(0) // -Infinity
Math.log2(-2) // NaN
Math.log2("1024")// 10
Math.log2("foo") // NaN
Math.log10()
**Math.log10()** 函数返回一个数字以 10 为底的对数.
如果传入的参数小于 0, 则返回 NaN.
Math.log10(10) // 1
Math.log10(100) // 2
Math.log10("100")// 2
Math.log10(1) // 0
Math.log10(0) // -Infinity
Math.log10(-2) // NaN
Math.log10("foo")// NaN
New Number Properties & New Number Methods
EPSILON
Number.EPSILON 属性表示 1 与Number可表示的大于 1 的最小的浮点数之间的差值。
EPSILON属性的值接近 2.2204460492503130808472633361816E-16 或 2的-52次方
EPSILON的特性: writable : false, enumerable: false, configurable: false
MIN_SAFE_INTEGER
Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER 代表在 JavaScript中最小的安全的integer型数字 (-(2的53次方 - 1)).
特性同EPSILON特性
Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER // -9007199254740991
-(Math.pow(2, 53) - 1) // -9007199254740991
MAX_SAFE_INTEGER
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER 常量表示在 JavaScript 中最大的安全整数(maxinum safe integer)(2的53次方 - 1)。
特性同EPSILON特性
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER // 9007199254740991
Math.pow(2, 53) - 1 // 9007199254740991
Number.isInteger()
Number.isInteger() 方法用来判断给定的参数是否为整数。
Number.isInteger(0); // true
Number.isInteger(1); // true
Number.isInteger(-100000); // true
Number.isInteger(0.1); // false
Number.isInteger(Math.PI); // false
Number.isInteger(Infinity); // false
Number.isInteger(-Infinity); // false
Number.isInteger("10"); // false
Number.isInteger(true); // false
Number.isInteger(false); // false
Number.isInteger([1]); // false
Number.isSafeInteger()
Number.isSafeInteger() 方法用来判断传入的参数值是否是一个“安全整数”(safe integer)。

Number.isSafeInteger(3); // true
Number.isSafeInteger(Math.pow(2, 53)) // false
Number.isSafeInteger(Math.pow(2, 53) - 1) // true
Number.isSafeInteger(NaN); // false
Number.isSafeInteger(Infinity); // false
Number.isSafeInteger("3"); // false
Number.isSafeInteger(3.1); // false
Number.isSafeInteger(3.0); // true
New Global Methods
isFinite()
该全局 isFinite() 函数用来判断被传入的参数值是否为一个有限数值(finite number)。在必要情况下,参数会首先转为一个数值。
可以用这个方法来判定一个数字是否是有限数字。isFinite 方法检测它参数的数值。如果参数是 NaN,正无穷大或者负无穷大,会返回false,其他返回 true。
isFinite(Infinity); // false
isFinite(NaN); // false
isFinite(-Infinity); // false
isFinite(0); // true
isFinite(2e64); // true, 在更强壮的Number.isFinite(null)中将会得到false
isFinite("0"); // true, 在更强壮的Number.isFinite('0')中将会得到false
isNaN()
isNaN() 函数用来确定一个值是否为NaN 。
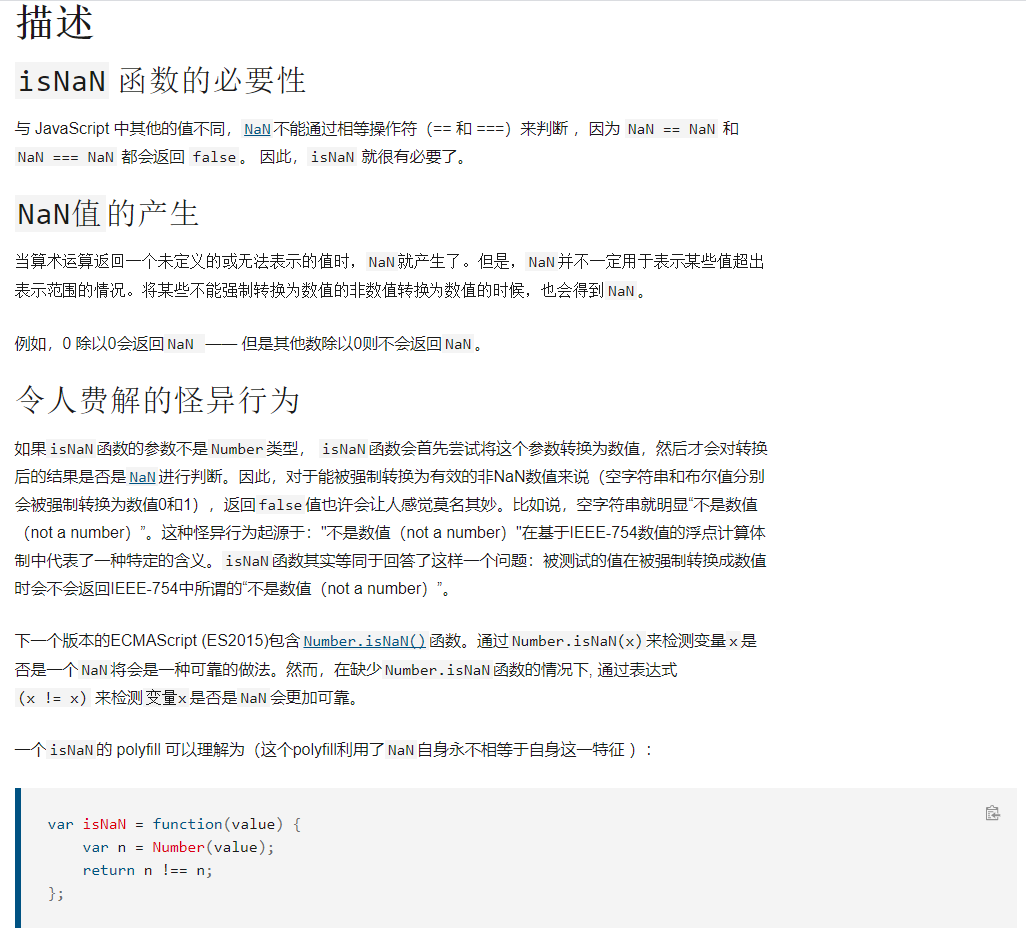
isNaN(NaN); // true
isNaN(undefined); // true
isNaN({}); // true
isNaN(true); // false
isNaN(null); // false
isNaN(37); // false
// strings
isNaN("37"); // false: 可以被转换成数值37
isNaN("37.37"); // false: 可以被转换成数值37.37
isNaN("37,5"); // true
isNaN('123ABC'); // true: parseInt("123ABC")的结果是 123, 但是Number("123ABC")结果是 NaN
isNaN(""); // false: 空字符串被转换成0
isNaN(" "); // false: 包含空格的字符串被转换成0
// dates
isNaN(new Date()); // false
isNaN(new Date().toString()); // true
isNaN("blabla") // true: "blabla"不能转换成数值
// 转换成数值失败, 返回NaN
JavaScriopt Modules
在ES6 JS引进了模块化。模块化也是很多框架的基本原理,将各种组件封装成模块然后导出。
细节不深究,理解什么是模块即可。
看这个网址查看更详细的有关Modules的内容:MDN



